reading-notes
Game of Greed Reading Part 3
List Comprehensions in Python
List comprehension is a powerful and concise method for creating lists in Python that becomes essential the more you work with lists, and lists of lists.
List comprehension offers a shorter syntax when you want to create a new list based on the values of an existing list.
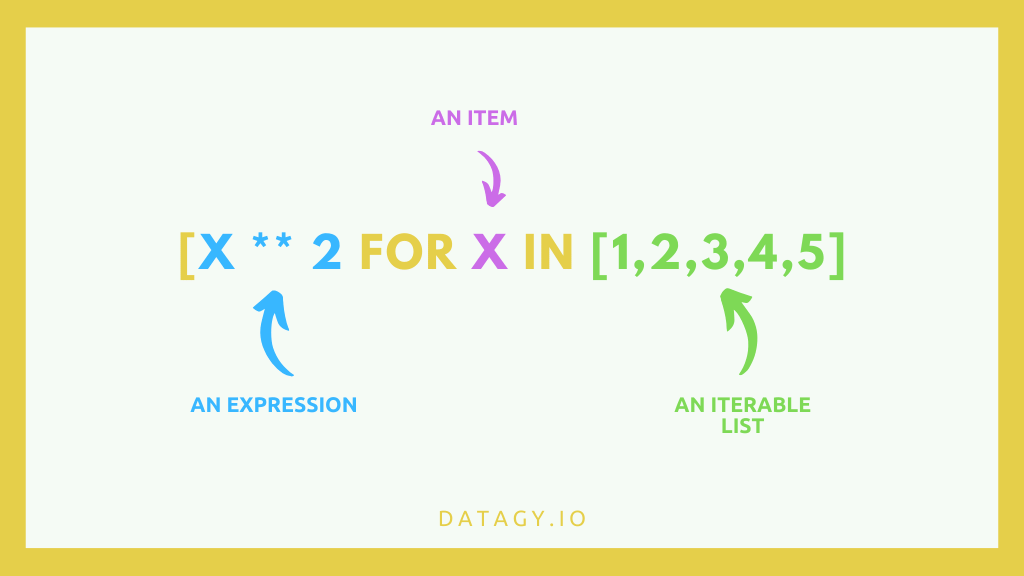
Syntax
my_new_list = [ expression for item in list ]
there are three parts in the expression above which are :
- the expression we’d like to carry out. expression inside the square brackets.
- the object that the expression will work on. item inside the square brackets.
- an iterable list of objects to build our new list from. list inside the square brackets.
Example for Creating a List Using Loops and List Comprehension in Python
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "kiwi", "mango"]
newlist = [x for x in fruits if "a" in x]
Example for condinditions in list comprehension
newlist = [x for x in fruits if x != "apple"]
in the example above, The condition if x != “apple” will return True for all elements other than “apple”
Example for Multiplying Parts of a List
multiples_of_three = [ x*3 for x in range(10) ]
Example for showing the first letter of each word using Python
letters = [ name[0] for name in authors ]
where authors is a list of strings .
Example for Lower/Upper case converter using Python
lower_case = [ letter.lower() for letter in ['A','B','C'] ]
upper_case = [ letter.upper() for letter in ['a','b','c'] ]
Example for Printing numbers only from a given string
user_data = "Elvis Presley 987-654-3210"
phone_number = [ x for x in user_data if x.isdigit()]
isdigit() is a python built-in method that checks if the string character is a digit or not
Summary
- List comprehension is an elegant way to define and create lists based on existing lists, it’s easier than the normal way
- List comprehension is generally faster than normal functions and loops for creating list.
- we should avoid writing very long list comprehensions in one line to ensure that code is user-friendly.
- every list comprehension can be rewritten in for loop, but every for loop can’t be rewritten in the form of list comprehension.
for more understanding of list comprehension in Python:
-
for loop in list comprehension:
-
for loop with if condition: